Updated on:
| Written by:
What Is RDIMM Memory?
RDIMM (Registered DIMM) Explained
RDIMM (Registered Dual Inline Memory Module) is a server-grade memory type that includes a register (or buffer) between the memory controller and the DRAM chips. This register handles command and address signals, reducing electrical load and improving signal integrity—especially critical in servers running multiple memory modules.
RDIMMs are defined by official standards like JEDEC’s RDIMM specifications, which outline electrical, timing, and interface requirements for DDR4 and DDR5 server memory.
For a detailed side-by-side, see our LRDIMM vs RDIMM vs UDIMM comparison that explains when to choose each type.
RDIMM vs. UDIMM vs. LRDIMM
| Module Type | Buffering | Capacity | Latency | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UDIMM | None | Low (2–4 ranks) | Lowest | Desktops, Entry Servers |
| RDIMM | Command/address only | Moderate to high (up to 8 ranks on DDR5, e.g., 256 GB) | Moderate | Most Servers, Workstations |
| LRDIMM | Full (Data + Ctrl) | Highest (up to 8 ranks, maximized electrical load reduction) | Highest | Memory-Dense Servers |
Where RDIMMs Are Used
- Virtualized environments (e.g., VMware, Proxmox)
- Data center servers with 256 GB+ memory needs
- High-reliability systems in telecom, HPC, or analytics
RDIMM Trade-Offs
- Latency: Slightly higher than UDIMM due to register delay
- Power: Minimal increase vs. UDIMM
- Compatibility: Not supported by most desktop motherboards
When Should You Choose RDIMM?
Use RDIMM if you:
- Run servers with >256 GB RAM per socket
- Need ECC and long uptime (e.g., Proxmox, ESXi)
- Want a stable middle ground between UDIMM and LRDIMM
Summary
RDIMM is the most common server memory type, offering a balance of capacity, stability, and cost. It’s perfect for systems that need more memory per CPU socket—without the added latency and power draw of LRDIMM. RDIMM is often the default memory type in Dell, HPE, and Lenovo servers due to its stability and scalability.
RDIMM Memory FAQ
What is RDIMM memory?
RDIMM (Registered DIMM) is a type of server memory that includes a register to buffer command and address signals between the memory controller and the DRAM chips. This improves stability and allows more memory modules per channel.
Can i use RDIMM instead of UDIMM?
No—RDIMM and UDIMM are not interchangeable. RDIMMs require motherboard support and are typically used in servers, while UDIMMs are common in desktops.
How to tell if memory is UDIMM or RDIMM?
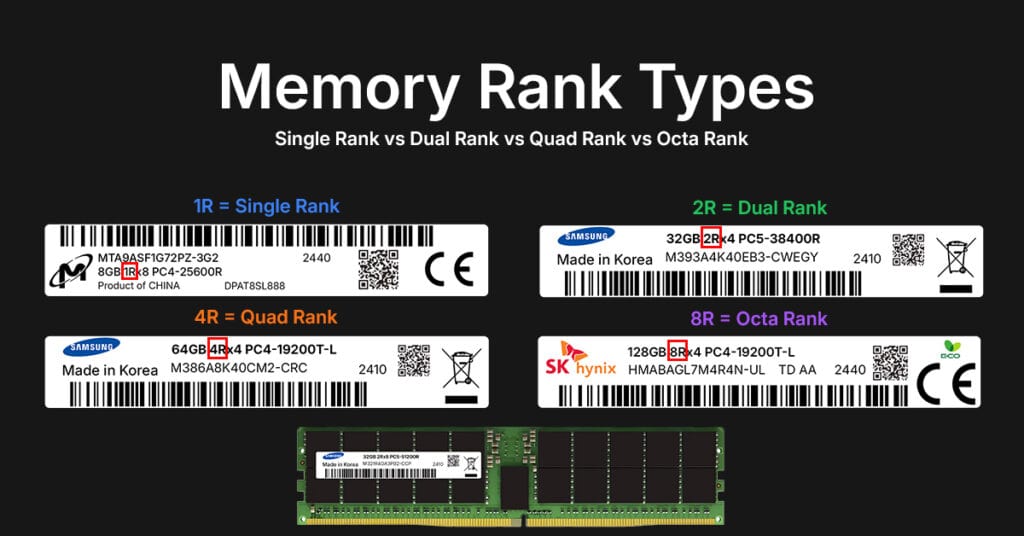
Check the label or part number: RDIMMs often include an “R” in the model name. You can also use system tools like dmidecode on Linux or CPU-Z on Windows to identify the memory type.
Is RDIMM ECC?
Yes, all RDIMMs are ECC (Error-Correcting Code) by default. They correct single-bit errors and detect multi-bit errors, which is critical in server and enterprise environments.
Is there such a thing as non-ECC RDIMM?
No—RDIMMs always include ECC. The registered design is built for reliability, and ECC is part of that standard.
What is 3DS RDIMM?
3DS RDIMM uses 3D-stacked DRAM (3DS) technology to support higher densities, such as up to 256 GB per module, while maintaining signal integrity. It’s often used in DDR4/DDR5 RDIMM configurations.
Can regular RDIMM be mixed with 3DS RDIMM?
No, mixing standard RDIMM with 3DS RDIMM is not supported and can cause system instability or memory errors. Use only one type per system.
About the Author

Edgars Zukovskis
Board Member | CoreWave Labs
14+ years of expertise helping telecom operators, datacenters, and system integrators build efficient, cost-effective networks using compatible hardware solutions.
Server Memory for Top Brands
Select Your Server Brand to Find Compatible Memory
Recommended Reads
Discover insights to power your infrastructure.